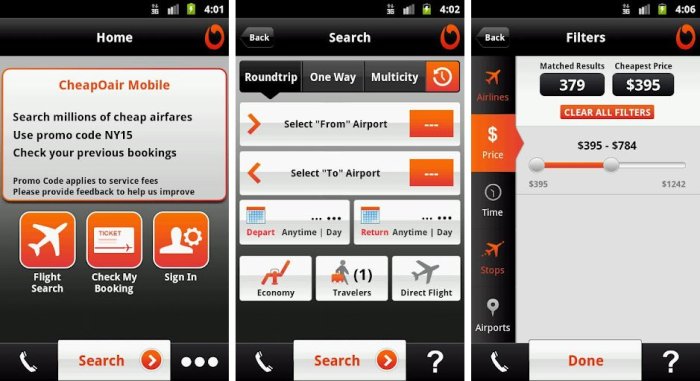
ai powered tax filing app for individuals Streamlining Taxes with AI
ai powered tax filing app for individuals represents a significant paradigm shift in how individuals approach their tax obligations. This evolution, fueled by advancements in artificial intelligence, promises to transform a traditionally complex and often daunting process into a more efficient, accurate, and user-friendly experience. The following text will delve into the intricacies of these applications, exploring their underlying mechanisms, features, security measures, and overall impact on both individual taxpayers and the tax preparation industry.
This comprehensive analysis will examine the fundamental concepts of AI in tax filing, dissecting the algorithms that power these applications and illustrating how they automate various aspects of the process, from data entry to deduction identification. Furthermore, we will compare and contrast these AI-driven solutions with traditional methods, evaluating their cost-effectiveness, user experience, and overall value proposition. Finally, we will consider the future trends and developments shaping the landscape of AI-powered tax filing, along with the implications for tax professionals and regulatory bodies.
Understanding the Fundamental Concepts of AI in Tax Filing for Individuals
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing tax filing for individuals, offering significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and user experience. This transformation is driven by sophisticated algorithms that automate tasks, identify opportunities, and minimize errors, ultimately simplifying a complex process.
Basic Principles of AI in Tax Filing
AI in tax filing leverages several core principles to streamline operations. These include machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and rule-based systems. Machine learning algorithms, such as supervised learning, are trained on vast datasets of tax returns to identify patterns and make predictions. Natural language processing enables the system to understand and interpret text-based information, such as tax forms and receipts.
Rule-based systems encode tax regulations and guidelines, ensuring compliance. These systems work together to automate tasks and provide accurate results.For example, a supervised learning algorithm might be trained on historical tax data to predict the likelihood of certain deductions based on an individual’s income, expenses, and other relevant factors. The algorithm learns from these examples, adjusting its parameters to improve its accuracy over time.
Natural language processing is used to extract key information from scanned documents, such as W-2 forms or 1099 forms, automatically populating the relevant fields in the tax return. Rule-based systems ensure that all calculations and deductions comply with current tax laws and regulations.AI also employs advanced techniques such as deep learning, a subset of machine learning that utilizes artificial neural networks with multiple layers to analyze data.
This allows for complex pattern recognition and more accurate predictions.
Automation of Tax Filing Functions
AI significantly enhances various aspects of tax filing through automation. These are specific ways AI assists individuals with their taxes:
- Data Entry Automation: AI automates data entry using optical character recognition (OCR) and natural language processing (NLP).
- Example: An individual uploads a W-2 form. The OCR system scans the document, and NLP extracts the relevant data (e.g., wages, taxes withheld) and automatically populates the corresponding fields in the tax return software. This eliminates the need for manual data entry, saving time and reducing the risk of human error.
- Identification of Potential Deductions: AI algorithms analyze an individual’s financial data to identify potential deductions and credits.
- Example: Based on the user’s income, expenses, and other information, the AI system may identify eligibility for deductions such as the student loan interest deduction, the child tax credit, or the home office deduction. The system prompts the user with relevant questions and guides them through the process of claiming these deductions. This ensures that users do not miss out on potential tax savings.
- Error Minimization: AI helps to minimize errors by performing calculations and checking for inconsistencies.
- Example: The AI system performs all necessary calculations automatically, such as calculating adjusted gross income (AGI) or total tax liability. The system also checks for inconsistencies, such as a mismatch between the reported income and the taxes withheld. This ensures the accuracy of the tax return and reduces the risk of errors that could lead to penalties or audits.
Advantages of AI Over Traditional Tax Preparation
The adoption of AI in tax preparation provides notable advantages compared to traditional methods. These include enhanced efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness.
- Time-Saving: AI significantly reduces the time required to prepare and file taxes.
- Example: Automating data entry and calculations can reduce tax preparation time from several hours to a few minutes, particularly for individuals with simple tax situations.
- Accuracy: AI minimizes errors through automated calculations and rule-based checks, resulting in more accurate tax returns.
- Example: AI systems can perform complex calculations with greater precision than humans, reducing the likelihood of errors that could lead to audits or penalties.
- Cost-Effectiveness: AI-powered tax filing tools can be more affordable than hiring a tax professional.
- Example: Many AI-powered tax filing applications offer free or low-cost options, making them accessible to a wider range of individuals, while professional tax preparation services can be expensive.
Exploring the Features and Functionality of AI-Powered Tax Filing Apps
AI-powered tax filing apps are transforming the landscape of personal finance, offering a streamlined and often more efficient alternative to traditional tax preparation methods. These applications leverage artificial intelligence to automate various aspects of the tax filing process, from data entry to tax liability calculation. This section will delve into the core features, user interface, and comparative analysis of several popular AI-powered tax filing applications, providing a comprehensive understanding of their capabilities and user experience.
Key Features of AI-Powered Tax Filing Apps
AI-powered tax filing applications are designed to simplify the complex process of tax preparation. They offer a suite of features that automate and optimize the filing experience. These features contribute to efficiency, accuracy, and user convenience.
- Document Scanning and Data Extraction: A crucial feature is the ability to scan and automatically extract data from tax documents. This utilizes Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and other AI techniques to identify and interpret information from W-2s, 1099s, and other relevant forms. This eliminates the need for manual data entry, reducing the potential for human error and saving time. For example, a user can simply take a photo of their W-2, and the app will automatically populate the necessary fields, such as income, taxes withheld, and employer information.
- Automated Form Filling: Once data is extracted, the app automatically populates the appropriate tax forms. The AI algorithms understand the structure and requirements of various tax forms, ensuring that information is entered correctly in the relevant sections. This is particularly beneficial for individuals unfamiliar with tax forms.
- Real-Time Tax Liability Estimation: A significant advantage is the ability to provide real-time estimates of tax liability or refund. As users input their income, deductions, and credits, the app dynamically calculates the tax implications. This feature allows users to understand the impact of their financial decisions on their tax situation throughout the year. The apps use complex algorithms to analyze the entered data, considering factors like filing status, dependents, and eligible deductions and credits.
- Deduction and Credit Identification: AI-powered apps often include features that help users identify potential deductions and credits they may be eligible for. These apps analyze the user’s financial data and provide personalized recommendations based on their circumstances. This can help users maximize their tax savings by claiming all eligible deductions and credits. For instance, the app might identify eligibility for the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) or the Child Tax Credit based on the user’s income and family situation.
- Error Checking and Audit Readiness: To ensure accuracy, these apps incorporate error-checking mechanisms. They flag potential errors or inconsistencies in the entered data, reducing the risk of filing an inaccurate return. Furthermore, some apps provide features that help users prepare for potential audits, such as storing documentation and providing explanations for claimed deductions and credits.
User Interface and User Experience
The user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) are critical for the usability and accessibility of AI-powered tax filing apps. These apps aim to be user-friendly, catering to individuals with varying levels of tax knowledge. The design principles often prioritize simplicity, clarity, and guidance throughout the tax filing process.
- Intuitive Navigation: The apps typically feature a clear and straightforward navigation system. Users can easily move through the different sections of the tax filing process, with logical organization and step-by-step instructions.
- Interactive Guidance: Many apps provide interactive guidance in the form of chatbots, tutorials, and helpful prompts. These features guide users through the process, explaining complex tax concepts in simple terms and answering common questions.
- Mobile Accessibility: Recognizing the importance of mobile access, most apps are designed to be fully functional on mobile devices. This allows users to file their taxes anytime, anywhere.
- Personalized Experience: The apps often personalize the experience based on the user’s profile and tax situation. This may involve tailoring the questions asked, providing relevant information, and highlighting deductions and credits specific to the user’s circumstances.
- Visual Aids: To enhance understanding, the apps may incorporate visual aids such as charts, graphs, and progress bars. These visual elements can help users track their progress, understand their tax situation, and visualize the impact of different financial decisions.
Comparison of AI-Powered Tax Filing Apps
The following table provides a comparison of key features across three popular AI-powered tax filing applications. This comparison focuses on functionalities like data security, customer support, and pricing, aiding in informed decision-making.
| Feature | App A | App B | App C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Security | 256-bit encryption, two-factor authentication | Multi-factor authentication, SOC 2 certified | Industry-standard encryption, secure data storage |
| Customer Support | Email, phone, live chat, extensive FAQ section | Live chat, email, knowledge base | Email, phone, community forums |
| Pricing (Federal Filing) | Free for simple returns, paid plans for more complex returns | Free for simple returns, premium plans with additional features | Free for all federal returns, additional fees for state filing |
| Document Scanning | Yes, with OCR technology | Yes, with advanced OCR capabilities | Yes, supports various document formats |
| Automated Form Filling | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Real-Time Tax Liability Estimation | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Data Security and Privacy Measures in AI-Driven Tax Filing Solutions: Ai Powered Tax Filing App For Individuals
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into tax filing applications offers significant advantages in terms of efficiency and accuracy. However, this advancement necessitates robust data security and privacy measures to safeguard sensitive financial information. Protecting user data is paramount, as breaches can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and reputational damage. This section delves into the specific security protocols, data handling practices, and user-centric measures employed by AI-driven tax filing solutions to mitigate these risks.
Data Security Measures Employed by AI-Powered Tax Filing Apps
AI-powered tax filing applications utilize a multi-layered approach to data security, incorporating various techniques to protect sensitive user information. This includes robust encryption protocols, secure data storage practices, and strict adherence to privacy regulations. These measures are critical in preventing unauthorized access, data breaches, and ensuring the confidentiality of user financial data.
- Encryption Protocols: Data encryption is a cornerstone of data security. AI-powered tax filing apps typically employ advanced encryption algorithms, such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with a key length of 256 bits, to protect data both in transit and at rest. This means that even if data is intercepted, it is rendered unreadable without the decryption key. For instance, when a user submits their tax information, it is encrypted using a secure protocol like Transport Layer Security (TLS/SSL) before being transmitted to the application’s servers.
- Data Storage Practices: Secure data storage is equally crucial. Tax filing apps often store user data on secure servers, such as those provided by cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure, which are designed with robust security features. These features include physical security measures (e.g., restricted access, surveillance), network security (e.g., firewalls, intrusion detection systems), and data redundancy (e.g., data backups, disaster recovery plans).
Furthermore, data is often stored in encrypted form within these secure environments.
- Compliance with Privacy Regulations: Compliance with privacy regulations is mandatory. AI-powered tax filing apps must adhere to various privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. These regulations dictate how user data is collected, processed, and stored, and they impose strict requirements on data security and user consent.
For example, apps must provide users with clear and transparent privacy policies, obtain explicit consent for data collection, and provide users with the right to access, correct, and delete their data.
Handling User Data in AI-Driven Tax Filing Solutions
The handling of user data by AI-driven tax filing solutions involves sophisticated techniques to protect user privacy while enabling the functionality of the application. This includes data anonymization, the establishment of clear data retention policies, and transparency in data usage. These practices are designed to minimize the risk of data breaches and ensure that user data is handled responsibly and ethically.
- Data Anonymization Techniques: Data anonymization is a crucial technique for protecting user privacy. This involves removing or altering personally identifiable information (PII) from data sets, making it difficult or impossible to identify individual users. For example, before any data analysis or model training is performed, sensitive information like names, addresses, and social security numbers are often removed or replaced with pseudonyms.
This allows developers to improve the AI models without compromising user privacy. Techniques such as data masking and generalization are frequently employed.
- Data Retention Policies: Data retention policies define how long user data is stored and when it is deleted. AI-powered tax filing apps typically have clearly defined data retention policies, specifying the duration for which different types of data are stored. These policies are often aligned with legal requirements and business needs. For example, some tax information might be retained for several years to comply with IRS regulations, while other less critical data might be deleted after a shorter period.
These policies should be clearly communicated to users in the app’s privacy policy.
- Transparency in Data Usage: Transparency in data usage is essential for building trust with users. AI-powered tax filing apps should provide clear and concise information about how user data is collected, used, and shared. This includes explaining what data is collected, why it is collected, how it is used to improve the app’s functionality, and whether it is shared with any third parties.
Users should have easy access to this information, typically through a privacy policy and/or a data usage dashboard within the app.
Potential Risks and User Protection Strategies
Despite robust security measures, potential risks remain. Data breaches and security vulnerabilities are threats that can affect any online application. However, users can take several steps to protect their information when using AI-powered tax filing apps. Implementing strong passwords and multi-factor authentication is crucial.
- Potential Risks: Data breaches can occur through various means, including cyberattacks (e.g., phishing, malware, ransomware), human error (e.g., accidental data leaks), and system vulnerabilities (e.g., software bugs). Even with advanced security measures, no system is entirely immune to these risks. The consequences of a data breach can be severe, including identity theft, financial loss, and reputational damage.
- User Protection Strategies: Users can significantly enhance their data security by following some basic but effective security practices. These include:
- Strong Passwords: Users should create strong, unique passwords for their tax filing accounts, incorporating a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. They should avoid using easily guessable information like birthdays or names.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enabling multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security. This typically involves verifying the user’s identity through a second factor, such as a code sent to their mobile phone or a biometric scan, in addition to their password. MFA makes it significantly more difficult for unauthorized individuals to access an account, even if they have the user’s password.
- Regular Software Updates: Ensure that the operating system and any software on the device used to access the tax filing app are up to date. Software updates often include security patches that fix known vulnerabilities.
- Awareness of Phishing: Be vigilant about phishing attempts. Never click on suspicious links or provide personal information in response to unsolicited emails or messages. Always access the tax filing app directly through its official website or mobile app.
Evaluating the Accuracy and Reliability of AI in Tax Filing
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into tax filing applications promises increased efficiency and accuracy. However, assessing the reliability of these AI systems requires a rigorous examination of their training, validation, and ongoing maintenance. This section delves into the methodologies employed to ensure the accuracy of AI-powered tax filing, highlighting both its capabilities and limitations.
Training and Validation of AI Algorithms
AI algorithms utilized in tax filing are not inherently accurate; their performance hinges on the quality and quantity of the data they are trained on. This training process involves feeding the AI system vast datasets of historical tax returns, tax laws, and regulations. The accuracy of the AI is dependent on the quality of this initial training phase.The process of training and validating AI algorithms involves several key steps:
- Data Acquisition and Preparation: This phase involves gathering extensive datasets of tax-related information, including tax forms (1040, W-2s, 1099s, etc.), tax codes, and regulatory updates from sources like the IRS and state tax agencies. Data is cleaned, formatted, and anonymized to protect user privacy.
- Algorithm Selection and Development: Depending on the specific task (e.g., calculating deductions, identifying eligible credits), different AI algorithms (e.g., machine learning models, natural language processing) are selected or developed. The choice of algorithm depends on its suitability for handling the complexity and nuances of tax regulations.
- Training the Model: The prepared data is used to train the selected AI model. The model learns to identify patterns, relationships, and correlations within the data. This process often involves iterative adjustments to the model’s parameters to optimize its performance. The AI learns to predict tax outcomes based on the input data.
- Testing and Validation: The trained model is rigorously tested using a separate dataset (test data) that was not used during training. This test data is designed to simulate real-world tax scenarios. Performance metrics such as accuracy, precision, and recall are calculated to evaluate the model’s performance.
- Continuous Learning and Improvement: AI models are continuously updated with new data and feedback to adapt to changes in tax laws and improve their accuracy over time. This involves retraining the model periodically and incorporating user feedback to refine its performance. This is achieved by updating the algorithms with changes in tax laws and regulations.
Limitations of AI in Tax Filing, Ai powered tax filing app for individuals
While AI offers significant advantages, it is not without limitations. Certain tax situations require human oversight due to their complexity or the ambiguity of tax regulations.AI’s limitations include:
- Complex Tax Scenarios: AI may struggle with intricate tax situations, such as those involving complex business structures, international tax matters, or unique investment strategies. These scenarios often involve nuanced interpretations of tax laws and require a level of judgment that AI may not yet possess.
- Ambiguous Tax Regulations: Tax laws can sometimes be open to interpretation, and AI may not be able to fully grasp the subtleties of these ambiguities. Human tax professionals can exercise judgment and provide advice based on their understanding of the specific context.
- Lack of Human Intuition: AI lacks the human intuition and experience to anticipate unforeseen tax issues or identify potential errors. A human tax professional can often identify issues that an AI system might miss.
- Data Dependency: The accuracy of AI-powered tax filing is dependent on the quality and completeness of the input data. Errors or omissions in the data can lead to inaccurate results.
Regular Updates and Changes in Tax Laws
Tax laws are subject to frequent changes, making it crucial for AI-powered tax filing apps to stay current. This is achieved through regular updates that incorporate changes in tax forms, regulations, and tax codes.The process of updating AI-powered tax filing apps involves:
- Monitoring Tax Law Changes: The app developers continuously monitor tax law changes from sources like the IRS, state tax agencies, and tax professionals.
- Updating Tax Forms and Algorithms: The developers update tax forms, algorithms, and tax codes to reflect changes in tax laws. This may involve modifying existing algorithms or creating new ones to address new tax rules.
- Testing and Validation: The updated algorithms and forms are rigorously tested using test data to ensure they function correctly and produce accurate results.
- Release of Updates: The updates are released to users, often through automatic updates or prompts within the app. Users are encouraged to install the updates to ensure their tax filing is compliant with current tax laws.
Comparing AI-Powered Tax Filing Apps with Traditional Tax Preparation Methods
The landscape of tax preparation has undergone a significant transformation with the advent of AI-powered applications. These innovative tools offer a compelling alternative to traditional methods, prompting a crucial examination of their respective strengths and weaknesses. Understanding the distinctions between AI-driven solutions and established practices is essential for individuals seeking the most efficient, cost-effective, and accurate approach to fulfilling their tax obligations.
This comparative analysis will delve into the nuances of each method, providing a comprehensive overview to inform informed decision-making.
Comparing AI-Powered Tax Filing Apps with Traditional Tax Software and Tax Professionals
The core difference between AI-powered tax filing apps and traditional methods lies in their underlying technologies and the level of human intervention. Traditional tax software relies on rule-based systems and user input to guide the filing process. Tax professionals, on the other hand, provide personalized advice and handle the entire process. AI-powered apps leverage machine learning to automate many aspects of tax preparation, potentially offering a blend of automation and guided support.Traditional tax software typically involves a more hands-on approach.
Users must manually enter their financial data and navigate the software’s interface, answering questions and selecting the appropriate tax forms. The level of user interaction can vary, with some software providing more guidance and support than others. Tax professionals offer a fully managed service, handling all aspects of tax preparation. They leverage their expertise to identify deductions, credits, and potential tax-saving opportunities.
The level of personalization and expertise provided by tax professionals is typically higher than what is available through traditional software. However, this comes at a premium cost. AI-powered apps aim to bridge the gap by offering automated data entry, intelligent recommendations, and user-friendly interfaces. The goal is to provide a user experience that is easier and more efficient than traditional software, while also offering a cost structure that is more competitive than hiring a tax professional.
However, the reliance on algorithms raises questions about accuracy and the ability to handle complex tax situations.
Cost-Effectiveness of AI-Powered Apps
The cost-effectiveness of AI-powered tax filing apps is a significant factor in their appeal. These apps often employ various pricing models, including free versions for simple tax situations, tiered pricing based on complexity, or subscription-based models. This contrasts with the often higher upfront costs of tax software or the fees charged by tax professionals. Potential savings can be substantial, particularly for individuals with straightforward tax situations.The value proposition for different user segments varies.
For individuals with simple tax returns, AI-powered apps offer a compelling value proposition due to their low cost and ease of use. Those with more complex tax situations may benefit from the additional features and support provided by paid versions or tax professionals. Consider the following: A user with only W-2 income and standard deductions might find a free AI-powered app sufficient.
However, a small business owner with multiple income streams, deductions, and credits might require the expertise of a tax professional or a more comprehensive paid version of a tax app. The potential for savings increases significantly for users with simple tax situations, as they can avoid the cost of tax software or professional fees. For example, if a user can save $200 by using an AI-powered app instead of hiring a tax preparer, that is a substantial saving.
The value proposition is also influenced by the user’s comfort level with technology and their willingness to handle the tax filing process independently.
Features, Costs, and User Experience: AI-Powered Apps vs. Tax Professionals
The following table provides a comparative analysis of AI-powered tax filing apps versus hiring a tax professional, highlighting key differences in features, costs, and user experience.
| Feature | AI-Powered Tax Filing Apps | Tax Professional |
|---|---|---|
| Features | Automated data entry, guided interview process, intelligent recommendations, error checking, integration with financial institutions, mobile accessibility, customer support (chat, email). | Personalized tax advice, tax planning, audit support, handling complex tax situations (investments, self-employment, etc.), direct communication, tax form preparation and filing. |
| Costs | Free (for simple returns), tiered pricing based on complexity, subscription-based models. | Hourly rates, per-form fees, flat fees, typically higher than AI-powered apps. |
| User Experience | User-friendly interface, intuitive navigation, step-by-step guidance, potential for self-service, reliance on user input. | Personalized service, direct interaction with a tax expert, less hands-on involvement, requires providing documentation and answering questions. |
| Accuracy and Reliability | Relies on algorithms and user input; accuracy depends on the app’s capabilities and the user’s data entry. | Higher level of accuracy due to professional expertise; responsibility for errors lies with the professional. |
The choice between these two methods hinges on individual circumstances, the complexity of the tax situation, and the desired level of support.
User Experience and Accessibility Considerations in AI-Driven Tax Filing
The success of AI-powered tax filing apps hinges not only on their computational prowess but also on their usability and accessibility. A well-designed user interface (UI) and a seamless user experience (UX) are crucial for user adoption and satisfaction. Furthermore, ensuring accessibility for users with disabilities is a legal and ethical imperative, broadening the reach and inclusivity of these tools.
This section delves into the design principles that govern the UI/UX of these apps, focusing on ease of use, intuitive navigation, and the implementation of accessibility features.
User Interface and User Experience Design Principles
The UI/UX design of AI-powered tax filing apps prioritizes simplicity and clarity. The goal is to demystify the complex process of tax filing, making it accessible to users with varying levels of tax knowledge. Intuitive navigation is paramount, guiding users through the filing process logically and efficiently. The design typically incorporates a clean and uncluttered layout, minimizing visual distractions and focusing on essential information.
Data entry fields are clearly labeled, with contextual help and tooltips provided to guide users. Progress indicators and clear visual cues offer reassurance and track the user’s progress. The overall design emphasizes a conversational approach, using plain language and avoiding technical jargon where possible.
Accessibility Features in AI-Powered Tax Filing Apps
Accessibility is a core design consideration, ensuring that tax filing apps are usable by individuals with disabilities. These features are implemented to conform to Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG).
- Screen Reader Compatibility: AI-powered tax filing apps are designed to be fully compatible with screen readers, allowing visually impaired users to navigate the app and understand the content. This includes providing appropriate alternative text for all images and graphical elements.
- Adjustable Font Sizes and Color Contrast: Users can customize the font size to improve readability. High contrast options are also available, allowing users to choose color schemes that are easier to perceive, catering to individuals with low vision or color blindness.
- Keyboard Navigation: The apps are fully navigable using a keyboard, enabling users with mobility impairments to interact with all elements without relying on a mouse.
- Alternative Text for Images: All images and visual elements include descriptive alternative text (alt text), providing context and meaning for screen reader users.
- Voice Control Compatibility: Some apps are designed to work with voice control software, allowing users to control the app using voice commands.
User Feedback on Accessibility and UX Design
User feedback is crucial for iterative improvement of the UI/UX and accessibility features.
“The step-by-step guidance was incredibly helpful. I was able to file my taxes in under an hour, which is a huge improvement over the hours I used to spend with paper forms.”
Positive feedback on ease of use and time-saving.
“The contrast on some of the buttons was too low, making it difficult to see them. I had to squint to read the labels.”
Negative feedback regarding color contrast and potential issues for users with low vision.
“I wish there was a way to save my progress and come back later. I had to finish everything in one sitting, which was challenging.”
Suggestion for improvement regarding saving progress.
“The app was very intuitive and easy to navigate. The screen reader worked perfectly.”
Positive feedback on screen reader compatibility.
Future Trends and Developments in AI-Powered Tax Filing for Individuals

The landscape of tax filing is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence. This evolution promises to redefine how individuals approach their tax obligations, leading to more efficient, accurate, and personalized experiences. Emerging technologies are poised to revolutionize various aspects of tax preparation, from data management to financial planning.
Integration of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is emerging as a critical component in enhancing the security and transparency of tax filing. This integration offers several key advantages.
- Secure Data Storage and Verification: Blockchain’s decentralized and immutable nature provides a secure platform for storing tax-related data. Each transaction or piece of information is recorded in a block and linked to the previous one, forming a chain. This structure makes it exceptionally difficult to tamper with or alter data, ensuring the integrity of tax records.
- Automated Compliance and Audit Trails: Smart contracts, self-executing contracts written on the blockchain, can automate compliance processes. For example, tax credits and deductions can be automatically verified based on predefined criteria, reducing the need for manual review and streamlining audits. Every step in the tax filing process can be traced and verified, providing a clear audit trail.
- Enhanced Privacy and Control: Blockchain technology allows individuals to maintain greater control over their tax data. They can selectively share information with tax authorities and other authorized parties while retaining ownership and control. This enhanced privacy is a significant benefit in an era of increasing data breaches.
Predictive Analytics in Tax Planning
Predictive analytics leverages historical data, current financial information, and external factors to forecast future tax liabilities and optimize tax strategies. This proactive approach offers substantial benefits to individual taxpayers.
- Personalized Tax Projections: AI algorithms can analyze an individual’s financial profile, including income, investments, and deductions, to generate personalized tax projections for the current and future tax years. These projections help individuals understand their potential tax obligations and plan accordingly.
- Identification of Tax-Saving Opportunities: By analyzing vast amounts of data, predictive analytics can identify potential tax-saving opportunities that individuals might overlook. This could include identifying eligible deductions, tax credits, or investment strategies that minimize tax liabilities.
- Risk Assessment and Compliance: Predictive models can also assess the risk of audits and identify areas where an individual’s tax filing may be inconsistent with regulations. This proactive risk assessment helps individuals avoid penalties and ensures compliance.
Personalized Tax Advice and Guidance
AI-powered systems are evolving to provide highly personalized tax advice and guidance, moving beyond simple data entry and calculation.
- AI-Driven Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Sophisticated chatbots and virtual assistants can provide real-time tax advice, answer questions, and guide individuals through the tax filing process. These systems are trained on vast datasets of tax laws and regulations, providing accurate and up-to-date information.
- Dynamic Tax Planning Recommendations: Based on an individual’s financial situation and goals, AI can generate dynamic tax planning recommendations. This could include advice on retirement savings, investment strategies, or charitable giving, tailored to maximize tax benefits.
- Integration with Financial Management Tools: AI-powered tax filing apps can integrate with financial management tools, such as budgeting apps and investment platforms. This integration allows for seamless data transfer and a holistic view of an individual’s financial situation, enabling more informed tax planning decisions.
Illustration: Futuristic AI-Powered Tax Filing Interface
The futuristic AI-powered tax filing interface will be characterized by a user-friendly design, interactive visualizations, and automated tax planning tools. The interface will feature a personalized dashboard that provides a comprehensive overview of an individual’s tax situation.
Dashboard Elements:
- Interactive Tax Summary: A visually appealing chart displays key tax metrics, such as estimated tax liability, deductions, and credits. The chart is interactive, allowing users to drill down into specific details. For instance, a user can click on “Deductions” to see a breakdown of itemized deductions, like medical expenses, charitable contributions, and state and local taxes. Each deduction category could have a small information icon that provides additional details on the deduction, or a link to resources for more information.
- Personalized Recommendations: A section displays personalized tax planning recommendations based on the user’s financial profile and goals. These recommendations could include suggestions for increasing retirement contributions, optimizing investment strategies, or identifying eligible tax credits. Each recommendation includes a clear explanation of the benefits and how to implement the strategy.
- Real-Time Tax Projections: A dynamic graph illustrates how changes in income, deductions, or credits will impact the user’s tax liability. Users can experiment with different scenarios, such as increasing their contributions to a 401(k) or donating to charity, to see how these actions will affect their tax bill.
Interactive Visualizations and Tools:
- Tax Deduction Explorer: A visual tool allows users to explore and understand various tax deductions. The tool presents deductions in a clear and concise format, with interactive elements that provide detailed explanations. Users can click on different deductions to learn about eligibility requirements and how to claim them.
- Tax Planning Simulator: A simulator allows users to model different financial scenarios and see how they will impact their tax liability. For example, a user could simulate the impact of selling stock, starting a business, or purchasing a home. The simulator provides real-time feedback on the tax implications of each scenario.
- AI-Powered Chatbot: An integrated chatbot provides real-time tax advice and answers questions. The chatbot can understand natural language queries and provide accurate and up-to-date information. It is accessible at all times, ensuring users have support when they need it.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations for AI-Powered Tax Filing Apps
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into tax filing introduces a complex web of compliance and regulatory requirements. These requirements are essential to ensure the integrity of the tax system, protect taxpayer rights, and maintain public trust. AI-powered tax filing apps must navigate a landscape shaped by data privacy regulations, tax law compliance, and financial reporting standards, all while adapting to evolving legal and ethical considerations.
Failure to comply can result in significant penalties, legal challenges, and damage to the app’s reputation.
Data Privacy Regulations and AI-Driven Tax Filing
Data privacy is a paramount concern in AI-powered tax filing. Apps handle sensitive personal and financial information, making them targets for cyberattacks and potential breaches of privacy. Compliance necessitates adherence to regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. These regulations mandate:
- Obtaining explicit consent from users for data collection and processing.
- Implementing robust security measures to protect data from unauthorized access or disclosure.
- Providing users with the right to access, rectify, and erase their personal data.
- Conducting data protection impact assessments to identify and mitigate privacy risks.
Tax filing apps must also comply with industry-specific regulations, such as those related to the handling of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and Protected Health Information (PHI), if applicable. This includes implementing data minimization strategies, only collecting and retaining data that is necessary for tax filing purposes, and ensuring data is stored securely. Regular audits and security assessments are crucial to demonstrate compliance and identify vulnerabilities.
Tax Law Compliance in AI-Powered Systems
Ensuring compliance with evolving tax laws is a critical challenge. Tax laws are complex, vary by jurisdiction, and are subject to frequent changes. AI-powered apps must be trained on up-to-date tax codes and regulations to accurately calculate tax liabilities and identify potential deductions and credits. This requires continuous monitoring and updating of the AI models to reflect changes in tax law.
- The IRS (Internal Revenue Service) in the United States, for example, has specific requirements for tax preparation software, including accuracy, security, and the ability to handle various tax forms and schedules.
- Tax apps must accurately interpret and apply tax laws, including those related to income, deductions, credits, and penalties.
- Proper documentation and audit trails are essential to demonstrate compliance and provide evidence of the accuracy of tax calculations.
Failure to comply with tax laws can lead to penalties for both the app provider and the user. Regular audits and reviews by tax professionals are vital to ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement.
Financial Reporting Standards and AI’s Role
Financial reporting standards, such as those set by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) in the United States, impact how AI-powered tax filing apps handle financial data. These standards govern the recognition, measurement, and disclosure of financial information, which is crucial for accurate tax filing.
- AI systems must be able to accurately classify and categorize financial transactions, following the guidelines set by accounting standards.
- Proper documentation and audit trails are required to demonstrate compliance with financial reporting standards.
- AI-driven apps should be able to generate reports that meet the requirements of financial reporting, such as income statements and balance sheets.
AI can improve the efficiency and accuracy of financial reporting, but it is important to ensure that the system follows established standards.
Government Oversight and Regulatory Bodies
Government agencies and regulatory bodies play a critical role in overseeing the development and deployment of AI-powered tax filing solutions. These bodies are responsible for enforcing regulations, protecting user rights, and ensuring the integrity of the tax system.
- The IRS in the United States, for example, is responsible for overseeing tax preparation software and ensuring compliance with tax laws.
- Regulatory bodies may conduct audits, reviews, and investigations to assess the accuracy, security, and compliance of AI-powered tax filing apps.
- These bodies also have the power to issue penalties, impose fines, and take legal action against app providers that fail to comply with regulations.
Collaboration between government agencies, app developers, and tax professionals is essential to establish clear guidelines and standards for AI-powered tax filing. This collaboration can help ensure that AI is used responsibly and ethically.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The use of AI in tax filing raises several legal and ethical considerations, including transparency, bias, and accountability. AI algorithms can be complex and difficult to understand, making it challenging for users to understand how their tax liabilities are calculated.
- Transparency is crucial to build trust and ensure that users can understand how the AI system works.
- AI algorithms can be biased, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. App developers must address bias in the training data and algorithms.
- Accountability is essential to ensure that there are mechanisms for addressing errors and holding app providers responsible for their actions.
Addressing these legal and ethical considerations is crucial to ensure that AI-powered tax filing apps are used responsibly and ethically. This requires a commitment to transparency, fairness, and accountability.
The Impact of AI on the Role of Tax Professionals
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into tax filing is fundamentally reshaping the roles and responsibilities of tax professionals. This shift, driven by advancements in machine learning and data processing, is transforming the traditional tax landscape, moving away from repetitive tasks towards a more strategic and client-focused approach. Tax professionals are adapting to leverage AI tools to enhance their services, ultimately improving efficiency and the quality of advice provided to clients.
Shifting Responsibilities: From Data Entry to Strategic Planning
AI is automating many of the manual tasks previously performed by tax professionals. This automation includes data entry, form filling, and basic calculations, freeing up professionals to focus on higher-value activities.
The automation of repetitive tasks is not just a technological upgrade; it’s a strategic reallocation of human capital.
This allows tax professionals to:
- Provide more in-depth tax planning and advisory services.
- Focus on complex tax situations requiring nuanced analysis.
- Develop personalized financial strategies for clients.
- Enhance client communication and relationship management.
This transition requires a re-evaluation of the skills required for success in the field.
Essential Skills and Competencies for Tax Professionals
To thrive in the age of AI, tax professionals must cultivate a new set of skills and competencies. These include proficiency in AI-powered tax tools, advanced data analysis capabilities, and strong client communication skills.
Adaptability and continuous learning are paramount for staying relevant in this evolving environment.
Key skills and competencies include:
- Proficiency in AI-Powered Tools: Understanding how to use and interpret the output of AI tax software, including data validation and identifying potential errors.
- Data Analysis: The ability to analyze large datasets to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies that can inform tax planning strategies. This includes the use of data visualization tools to communicate complex information effectively.
- Client Communication: Communicating complex tax information clearly and concisely to clients, building trust and providing personalized advice.
- Strategic Thinking: Developing proactive tax planning strategies that leverage AI insights to optimize financial outcomes for clients.
- Continuous Learning: Staying updated on the latest AI advancements, tax regulations, and industry best practices.
Illustration: A Futuristic Tax Office
The illustration depicts a modern, technologically advanced tax office where a tax professional is leveraging AI tools to serve clients. The scene emphasizes collaboration, data-driven insights, and personalized service.The office setting is bright and airy, with minimalist design elements. Large, curved interactive displays dominate the workspace, displaying real-time tax data visualizations, financial projections, and client information. The tax professional, dressed in professional attire, is seated at a sleek, ergonomic desk.
On the desk, there is a holographic projector displaying 3D models of financial data. The professional is using a touch-screen interface to interact with an AI-powered tax analysis platform. The platform displays tax return data, flagged anomalies, and potential tax-saving opportunities. The professional is consulting with a client, whose image is displayed on one of the interactive screens, engaging in a virtual meeting.
The client’s profile includes details like investment portfolios, property ownership, and income sources. The AI system analyzes this information and generates personalized tax advice in real time. The office environment also includes collaborative spaces for team meetings, featuring interactive whiteboards and integrated communication systems. The atmosphere is collaborative and client-centric, showcasing the integration of AI to enhance the quality of tax services.
This scene represents the transformation of tax professionals into advisors who use AI to deliver tailored financial strategies, making the tax process more efficient, accurate, and client-focused.
Closure
In conclusion, the advent of ai powered tax filing app for individuals marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of tax preparation. By leveraging the power of AI, these applications offer a compelling blend of efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility, potentially reshaping the way individuals manage their taxes. As technology continues to advance, the integration of AI in tax filing is poised to become even more sophisticated, offering personalized advice, proactive tax planning, and seamless integration with other financial tools.
The journey toward a more streamlined and intelligent tax experience is well underway, and its impact on both taxpayers and the industry promises to be profound.
FAQ Section
How accurate are AI-powered tax filing apps?
AI-powered apps are generally very accurate, relying on algorithms trained on vast datasets and regularly updated to reflect current tax laws. However, the accuracy depends on the quality of the data entered and the complexity of the user’s tax situation. Human review is often recommended for complex scenarios.
Are AI-powered tax filing apps secure?
Yes, reputable AI-powered tax filing apps employ robust security measures, including encryption, secure data storage, and compliance with privacy regulations. Users should still take precautions like using strong passwords and enabling multi-factor authentication.
Can AI-powered apps handle all types of tax situations?
While AI-powered apps are suitable for many tax situations, they may not be ideal for highly complex scenarios involving multiple income sources, investments, or unique deductions. In such cases, a tax professional might be necessary.
How do AI-powered apps handle changes in tax laws?
AI-powered tax filing apps are regularly updated to reflect changes in tax laws. Developers continuously update the algorithms and tax forms to ensure compliance. Users typically receive these updates automatically.