What is a data loss prevention (DLP) solution for cloud? It’s a crucial component in today’s digital landscape, where data resides increasingly in cloud environments. This overview dives into the world of cloud DLP, exploring its purpose, functionality, and the critical role it plays in safeguarding sensitive information. The rise of cloud computing has brought unprecedented flexibility and scalability, but it has also introduced new challenges for data security.
Cloud DLP solutions are designed to address these challenges by identifying, monitoring, and protecting sensitive data stored and accessed within cloud platforms. This includes everything from data in transit to data at rest, ensuring compliance with regulations and mitigating the risks of data breaches. This comprehensive guide will break down the essential components, features, and benefits of cloud DLP, providing you with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of cloud data security.
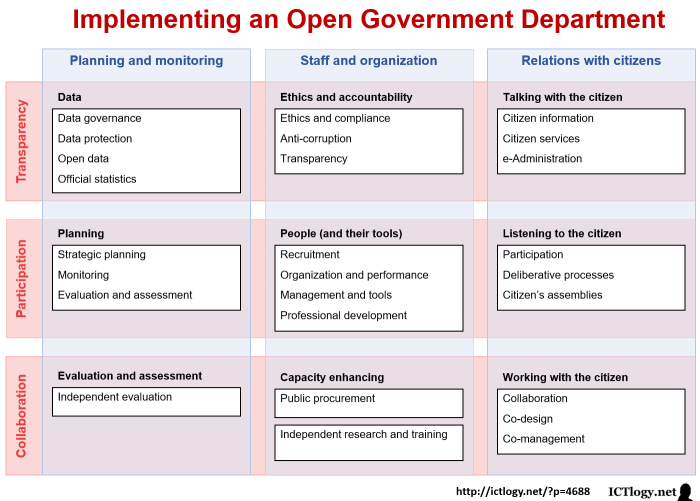
Defining Data Loss Prevention (DLP) for Cloud Environments
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions are critical for safeguarding sensitive information, and their application within cloud environments has become increasingly important. As organizations migrate their data and operations to the cloud, the need to protect this data from unauthorized access, loss, or theft becomes paramount. This section will delve into the core concepts of DLP specifically designed for cloud platforms, providing a clear understanding of its purpose and how it differs from traditional, on-premise DLP solutions.
Fundamental Concept of Cloud DLP
Cloud DLP, at its core, is a set of security measures designed to prevent sensitive data from leaving an organization’s control. It identifies, monitors, and protects confidential information wherever it resides: in transit, at rest, or in use within cloud environments. This involves scanning and analyzing data to detect policy violations, such as the unauthorized sharing of Personally Identifiable Information (PII), financial data, or intellectual property.
The goal is to minimize the risk of data breaches, compliance violations, and reputational damage. Cloud DLP solutions are designed to integrate seamlessly with various cloud services, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) offerings.
Definition of Cloud DLP and Primary Objectives
Cloud Data Loss Prevention (DLP) can be concisely defined as a security strategy and set of technologies used to ensure sensitive data within cloud environments is protected from loss, theft, or misuse. It encompasses a range of capabilities, including data discovery, classification, monitoring, and enforcement. The primary objectives of cloud DLP are:
- Data Visibility and Control: To gain comprehensive visibility into where sensitive data resides within the cloud and to exert control over its usage. This includes understanding data storage locations, access patterns, and data flows.
- Data Classification and Identification: To automatically identify and classify sensitive data based on predefined policies or custom rules. This enables organizations to understand the type and sensitivity of data they possess.
- Policy Enforcement: To enforce data security policies and prevent unauthorized data exfiltration or misuse. This may involve blocking or quarantining sensitive data transfers, encrypting data, or alerting security teams to policy violations.
- Compliance Support: To assist organizations in meeting regulatory compliance requirements, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, by providing tools for data protection and audit trails.
- Incident Response: To facilitate rapid incident response by providing detailed information about data breaches and enabling security teams to take swift action to contain and remediate the damage.
Core Differences Between On-Premise DLP and Cloud-Based DLP Solutions
While both on-premise and cloud-based DLP solutions share the fundamental goal of protecting sensitive data, they differ significantly in their architecture, deployment, and management. These differences are crucial to consider when choosing a DLP solution for a cloud environment.
- Deployment and Infrastructure: On-premise DLP solutions are deployed and managed within an organization’s own data centers, requiring significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and IT resources. Cloud-based DLP solutions, on the other hand, are typically delivered as a service, reducing the need for on-premise infrastructure and allowing for greater scalability and flexibility.
- Data Visibility and Coverage: On-premise DLP solutions may have limited visibility into data residing in cloud environments. Cloud-based DLP solutions are designed to integrate with various cloud services, providing comprehensive data visibility and coverage across different cloud platforms and applications.
- Scalability and Agility: Cloud-based DLP solutions offer greater scalability and agility compared to on-premise solutions. They can easily adapt to changing data volumes and business needs, allowing organizations to scale their data protection capabilities up or down as required. On-premise solutions often require significant time and resources to scale.
- Management and Maintenance: Cloud-based DLP solutions are typically managed and maintained by the vendor, reducing the burden on internal IT teams. On-premise solutions require organizations to handle all aspects of management, including software updates, security patches, and infrastructure maintenance.
- Cost: Cloud-based DLP solutions often have a lower total cost of ownership (TCO) compared to on-premise solutions due to reduced infrastructure costs, lower IT overhead, and the pay-as-you-go pricing model. On-premise solutions involve significant upfront capital expenditures and ongoing operational costs.
- Integration and Compatibility: Cloud-based DLP solutions are designed to seamlessly integrate with various cloud services and applications. On-premise solutions may have limited integration capabilities with cloud environments, requiring custom integrations and workarounds.
Key Components of a Cloud DLP Solution
A robust cloud Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solution is not a single product but rather a system comprised of several interacting components. These components work in concert to identify, monitor, and protect sensitive data residing in the cloud. Understanding these elements is crucial for effectively deploying and managing a DLP strategy.
Data Discovery and Classification
Data discovery and classification are fundamental processes within a cloud DLP solution, acting as the initial step in understanding and managing sensitive data. This involves identifying where sensitive data resides and categorizing it based on its type and sensitivity level.Data discovery methods include:
- Scanning Cloud Storage: DLP solutions scan cloud storage services like Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage, and Google Cloud Storage to identify data at rest. This scanning process analyzes the content of files and objects.
- Monitoring Data in Transit: Examining data as it moves across the network, including email, file transfers, and application usage. This often involves inspecting network traffic and application logs.
- Utilizing Cloud Provider APIs: Integrating with cloud provider APIs to gain insights into data storage, access patterns, and user activities. This can improve the accuracy of discovery and classification.
Data classification involves assigning labels or tags to data based on its sensitivity. This can be done manually, automatically, or through a combination of both. Classification methods include:
- Predefined Data Categories: DLP solutions often come with predefined categories for common data types, such as Personally Identifiable Information (PII) like social security numbers or credit card numbers, and Protected Health Information (PHI).
- Regular Expression Matching: Using regular expressions (regex) to identify patterns in data, such as credit card numbers, email addresses, or specific s. For example, a regex like
\b[0-9]3-[0-9]2-[0-9]4\bcould identify US social security numbers. - and Phrase Matching: Searching for specific s or phrases that indicate sensitive information. For instance, a document containing the phrase “confidential financial report” would likely be classified as sensitive.
- Data Fingerprinting: Creating a unique “fingerprint” of a data file or document. This allows the DLP solution to identify exact matches or near matches, even if the data has been slightly modified.
- Machine Learning (ML) and Natural Language Processing (NLP): Employing ML and NLP to automatically classify data based on its content and context. This is particularly useful for unstructured data, such as documents and emails.
Data classification facilitates the application of appropriate policies and controls. For example, data classified as “highly confidential” might be subject to stricter access controls and encryption requirements compared to data classified as “public.”
Data Monitoring and Real-Time Alerting
Data monitoring and real-time alerting are crucial for a cloud DLP solution to detect and respond to potential data breaches or policy violations promptly. This involves continuously observing data activity and generating alerts when suspicious or unauthorized actions occur.Data monitoring involves:
- Monitoring User Activity: Tracking user actions, such as file access, data uploads, downloads, and sharing activities. This includes monitoring user behavior across various cloud services.
- Monitoring Data Movement: Observing data as it moves within the cloud environment, between cloud services, and to external destinations.
- Analyzing Network Traffic: Inspecting network traffic to identify potential data exfiltration attempts or unauthorized data transfers. This can include monitoring for suspicious outbound connections or large data transfers.
- Logging and Auditing: Collecting and analyzing logs from cloud services, applications, and security tools to gain insights into data access and usage.
Real-time alerting is the immediate response to detected policy violations. Alerting mechanisms include:
- Policy Enforcement: DLP solutions enforce predefined policies to prevent data loss. These policies define rules for data access, sharing, and movement. For example, a policy might block the upload of sensitive data to an unauthorized cloud storage location.
- Alerting Mechanisms:
- Email Notifications: Sending email alerts to security teams or administrators when policy violations occur.
- SIEM Integration: Integrating with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to centralize alerts and enable security teams to correlate DLP events with other security events.
- Dashboard Visualization: Displaying alerts and real-time data on dashboards to provide security teams with a clear overview of potential data loss incidents.
- Incident Response: Initiating incident response workflows to address policy violations, such as quarantining files, blocking user access, or notifying relevant stakeholders.
Real-time alerting capabilities can significantly reduce the impact of data breaches. For instance, if a DLP solution detects an attempt to download a large amount of sensitive data, it can immediately alert the security team, allowing them to investigate and potentially prevent the data from leaving the cloud environment. A 2023 report by IBM estimated that the average cost of a data breach was $4.45 million.
Prompt detection and response through real-time alerting can help mitigate these costs.
Data Security Challenges in Cloud Environments
Cloud environments, while offering significant benefits in terms of scalability and cost-efficiency, introduce unique data security challenges that organizations must address. The distributed nature of cloud infrastructure, combined with the shared responsibility model, necessitates a proactive and comprehensive approach to data protection. Understanding these challenges is crucial for implementing effective data loss prevention (DLP) solutions.
Risks in Data Storage, Transit, and Access
The cloud presents distinct security risks across different phases of data’s lifecycle: storage, transit, and access. Each phase has its own set of vulnerabilities that malicious actors can exploit. A robust DLP strategy must address these varied risks to ensure comprehensive data protection.
Data Storage Risks
Data stored in the cloud is vulnerable to various threats. These include unauthorized access, data breaches, and data loss due to misconfiguration or vulnerabilities in the cloud provider’s infrastructure.
- Misconfiguration: Incorrectly configured storage buckets or databases can expose sensitive data to the public internet. For example, an Amazon S3 bucket configured with public read access could allow anyone to download the data stored within.
- Insider Threats: Malicious or negligent employees or contractors with access to cloud storage can steal or inadvertently leak sensitive information.
- Malware and Ransomware: Cloud storage can be targeted by malware and ransomware attacks, encrypting data and demanding ransom payments.
- Data Breaches: Exploitation of vulnerabilities in the cloud provider’s systems or applications can lead to data breaches, compromising sensitive information.
Data Transit Risks
Data in transit, moving between the user and the cloud provider or between different cloud services, is also at risk. Interception, eavesdropping, and tampering are potential threats.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Attackers can intercept data in transit, gaining access to sensitive information such as login credentials or financial data.
- Unencrypted Communication: Data transmitted over unencrypted channels is easily intercepted and read. Secure protocols like HTTPS are essential for protecting data in transit.
- Data Tampering: Attackers can modify data in transit, potentially causing damage or manipulating information.
- Compromised APIs: Weaknesses in APIs used to transfer data can be exploited to gain unauthorized access or modify data.
Data Access Risks
Controlling access to data is crucial for preventing unauthorized use or disclosure. Inadequate access controls and weak authentication mechanisms can create significant security vulnerabilities.
- Weak Authentication: Weak passwords or the lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA) can allow attackers to compromise user accounts and gain access to sensitive data.
- Privilege Escalation: Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities to gain elevated privileges, enabling them to access more data than they are authorized to see.
- Unintentional Data Exposure: Overly permissive access controls can inadvertently expose data to unauthorized users.
- Compromised Credentials: Stolen or compromised credentials can provide attackers with legitimate access to cloud resources and data.
Common Data Loss Scenarios
Several scenarios commonly lead to data loss in cloud environments. Understanding these scenarios helps organizations prioritize their DLP efforts and implement appropriate safeguards.
- Accidental Data Exposure: A user mistakenly shares a sensitive document with the wrong recipient or uploads it to a public cloud storage location. For example, an employee inadvertently emails a spreadsheet containing customer data to an external address.
- Malicious Insider Activity: A disgruntled employee steals confidential data before leaving the company.
- Data Breach Due to a Cloud Provider Vulnerability: A vulnerability in the cloud provider’s infrastructure is exploited, leading to a data breach.
- Ransomware Attack: Ransomware encrypts data stored in the cloud, rendering it inaccessible until a ransom is paid. In 2023, ransomware attacks increased significantly, impacting numerous organizations across various industries, with healthcare and financial sectors being major targets.
- Phishing Attacks: Phishing attacks compromise user credentials, allowing attackers to access cloud resources and steal data.
How Cloud DLP Solutions Work
Cloud Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions operate as a critical layer of defense, designed to monitor, detect, and prevent sensitive data from leaving a cloud environment without authorization. They achieve this through a combination of technologies and processes, working in real-time to protect data in transit, at rest, and in use. Understanding the operational mechanics of these solutions is key to appreciating their value in safeguarding cloud-based information assets.
Operational Processes of a Typical Cloud DLP Solution
The operation of a cloud DLP solution involves a multi-faceted approach to data security. This encompasses various stages, from initial configuration to ongoing monitoring and incident response. The following Artikels the typical operational flow:
- Data Discovery and Classification: The process begins with identifying and classifying sensitive data residing within the cloud environment. This often involves scanning data repositories, such as databases, file storage, and email systems, to locate data that falls under pre-defined sensitivity categories (e.g., Personally Identifiable Information (PII), Protected Health Information (PHI), financial data). This step is critical because it sets the foundation for subsequent monitoring and enforcement actions.
- Policy Definition and Enforcement: Security policies are established to dictate acceptable data handling practices. These policies are then enforced by the DLP solution. Policies can specify actions like blocking, quarantining, encrypting, or alerting, based on the type of data, the user accessing it, and the destination to which it is being sent. For instance, a policy might prevent the upload of credit card numbers to a public cloud storage service.
- Monitoring and Detection: The DLP solution continuously monitors data movement and user activity within the cloud environment. It analyzes data in transit (e.g., network traffic, email), at rest (e.g., stored files), and in use (e.g., applications accessing data). This monitoring process utilizes various techniques, including content inspection, context analysis, and user behavior analysis.
- Incident Response: When a policy violation is detected, the DLP solution triggers an incident response. This can involve automated actions (e.g., blocking a file transfer) and/or notifications to security teams. Incident response workflows are often customizable, allowing organizations to define specific actions based on the severity and nature of the violation. This may include quarantining the data, notifying the user, or escalating the incident to security personnel for further investigation.
- Reporting and Auditing: The solution generates detailed reports and audit logs that provide visibility into data security activities. These reports can be used to track policy compliance, identify potential vulnerabilities, and demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements. This reporting capability is essential for continuous improvement and risk management.
How Cloud DLP Systems Identify and Prevent Unauthorized Data Movement
Cloud DLP systems utilize a variety of techniques to identify and prevent the unauthorized movement of sensitive data. These techniques are designed to address different attack vectors and data loss scenarios.
- Content Inspection: This involves examining the content of data to identify sensitive information. DLP solutions employ techniques like matching, regular expressions, and data fingerprinting to detect specific patterns and data types. For example, a DLP system can be configured to scan outgoing emails for social security numbers, credit card numbers, or other sensitive data formats.
- Context Analysis: DLP solutions analyze the context surrounding data movement, considering factors like the user, the application, the destination, and the time of day. This helps to differentiate between legitimate and malicious data transfers. For example, a system might allow an employee to download a file to their company-issued laptop but block the same file from being uploaded to a personal cloud storage account.
- User Behavior Analysis (UBA): UBA monitors user activities and identifies anomalies that may indicate a data breach or insider threat. By establishing a baseline of normal user behavior, the system can detect deviations that warrant further investigation. This can include unusual file access patterns, excessive data downloads, or suspicious login attempts.
- Data Loss Prevention Agents: In some cloud DLP implementations, agents are installed on endpoints or servers to monitor data movement locally. These agents can block unauthorized file transfers, encrypt data, and enforce security policies. This approach provides a more granular level of control and protection.
- Integration with Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) and Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB): DLP solutions often integrate with CSPM and CASB tools to provide a more comprehensive security posture. CSPM tools help identify misconfigurations and vulnerabilities in cloud environments, while CASBs provide visibility and control over cloud applications. This integration allows for a more holistic approach to data security.
Methods Cloud DLP Uses to Enforce Data Security Policies
Cloud DLP solutions employ various methods to enforce the data security policies defined by an organization. These methods are designed to prevent data breaches and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Blocking: The most direct method of enforcement, blocking prevents unauthorized data movement. This can involve blocking file transfers, email transmissions, or access to specific cloud services. For example, a DLP system might block an employee from sending an email containing credit card numbers to an external recipient.
- Quarantine: When a policy violation is detected, the DLP solution can quarantine the data, preventing it from being accessed or transmitted further. This can be useful for containing potential breaches and allowing security teams to investigate the incident. The quarantined data can be stored in a secure location for analysis.
- Encryption: DLP solutions can encrypt sensitive data to protect it from unauthorized access. This can be applied to data at rest (e.g., stored files) or data in transit (e.g., email attachments). Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be read without the proper decryption key.
- Redaction: DLP can redact or mask sensitive information within documents or data streams. This is useful when data needs to be shared, but certain sensitive elements need to be removed. For example, a DLP system might redact a social security number from a document before it is shared with an external party.
- Alerting and Logging: DLP solutions generate alerts and logs to notify security teams of policy violations. These alerts can be customized to include detailed information about the incident, such as the user, the data involved, and the action taken. The logs provide a comprehensive audit trail of data security activities.
- Integration with Other Security Tools: DLP solutions can integrate with other security tools, such as SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems, to provide a more comprehensive security posture. This integration allows for centralized monitoring, analysis, and response to security incidents. This ensures that DLP events are correlated with other security events, providing a more holistic view of the organization’s security posture.
Features and Functionalities of Cloud DLP
Cloud Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions offer a comprehensive suite of features designed to protect sensitive data residing in cloud environments. These features go beyond basic data discovery and monitoring, providing robust capabilities for data classification, policy enforcement, and incident response. Understanding these functionalities is crucial for selecting a DLP solution that effectively addresses an organization’s specific data security needs and risk profile.
Key Features Found in Leading Cloud DLP Solutions
Leading cloud DLP solutions boast a variety of features that contribute to comprehensive data protection. These features work in concert to identify, monitor, and secure sensitive data across various cloud services and applications.
- Data Discovery and Classification: This feature involves scanning cloud storage and applications to identify and classify sensitive data based on content, context, and metadata. It helps organizations understand where their sensitive data resides.
- Policy Enforcement: Cloud DLP solutions allow administrators to define and enforce data security policies. These policies dictate how sensitive data can be accessed, stored, and shared.
- Monitoring and Alerting: Continuous monitoring of data activity is a core function. DLP solutions generate alerts when policy violations occur, enabling timely intervention.
- Data Loss Prevention: This involves preventing sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control, such as blocking the upload of sensitive files to public cloud storage or preventing the sharing of confidential information via email.
- Incident Response: When a data breach or policy violation is detected, DLP solutions provide tools and workflows to investigate and remediate incidents.
- Reporting and Analytics: Comprehensive reporting capabilities provide insights into data security posture, policy compliance, and incident trends.
- Integration with Cloud Services: Seamless integration with various cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) and applications (e.g., Salesforce, Microsoft 365) is essential for effective DLP.
Comparison of Cloud DLP Features
The features of cloud DLP solutions vary between vendors. The following table provides a comparative overview of key features, their descriptions, associated benefits, and examples of vendors that offer these capabilities.
| Feature | Description | Benefits | Vendor Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Discovery and Classification | Scans data repositories to identify and classify sensitive data, such as PII, PHI, and financial data. Uses content-based and context-based classification techniques. | Provides visibility into sensitive data locations, facilitates policy creation, and helps meet compliance requirements. | Varonis, Forcepoint, McAfee |
| Policy Enforcement | Allows administrators to define and enforce data security policies based on data classification, user roles, and other criteria. | Enforces data governance rules, reduces the risk of data breaches, and improves compliance. | Symantec, Microsoft, Google Cloud DLP |
| Monitoring and Alerting | Monitors data activity in real-time and generates alerts when policy violations occur. Provides detailed information about incidents. | Enables timely response to data security incidents, reduces the impact of breaches, and facilitates incident investigation. | Proofpoint, Digital Guardian, Zscaler |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Prevents sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control. Includes features such as blocking data exfiltration, preventing unauthorized data sharing, and enforcing data encryption. | Protects against data breaches, reduces the risk of data theft, and helps maintain data confidentiality. | Broadcom, Netskope, Trend Micro |
| Incident Response | Provides tools and workflows for investigating and remediating data security incidents. Includes features such as incident tracking, reporting, and remediation actions. | Streamlines incident response processes, reduces the time to resolve incidents, and minimizes the impact of breaches. | Rapid7, Splunk, IBM |
| Reporting and Analytics | Generates reports and provides analytics on data security posture, policy compliance, and incident trends. | Provides insights into data security risks, helps track compliance, and supports data-driven decision-making. | Imperva, Datadog, Sumo Logic |
| Integration with Cloud Services | Seamlessly integrates with various cloud platforms and applications, such as AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Salesforce, and Microsoft 365. | Provides comprehensive data protection across all cloud environments, simplifies management, and reduces the need for multiple security tools. | Cloudflare, CrowdStrike, Palo Alto Networks |
Advanced Features of Cloud DLP Solutions
Cloud DLP solutions offer advanced features that enhance data protection capabilities. These features provide granular control over sensitive data and further reduce the risk of data breaches.
Advanced features, such as data encryption and rights management, are crucial for comprehensive data protection. Data encryption transforms sensitive data into an unreadable format, rendering it useless to unauthorized users. This is especially important for data at rest and in transit. Rights management allows organizations to control who can access, modify, and share sensitive data, even after it leaves the organization’s control. This is often achieved through digital rights management (DRM) technologies, which enforce access restrictions and prevent unauthorized use. These advanced features, when implemented correctly, can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. For instance, a healthcare provider could use encryption to protect patient data stored in the cloud and rights management to control access to those records, ensuring only authorized personnel can view or modify them.
Implementation Strategies for Cloud DLP
Implementing a cloud Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solution requires careful planning and execution to ensure its effectiveness and minimize disruption to existing cloud operations. This section Artikels best practices, a step-by-step integration procedure, and recommendations for a successful deployment.
Best Practices for Implementing a Cloud DLP Solution
Adhering to best practices is crucial for maximizing the benefits of a cloud DLP solution and mitigating potential risks. These practices cover various aspects of the implementation process, from initial planning to ongoing management.
- Assess Your Data and Risk Profile: Before deploying a cloud DLP solution, conduct a thorough assessment of your data landscape. Identify where sensitive data resides, understand how it’s used, and determine the potential risks associated with its loss or exposure. This assessment informs the policies and configurations of your DLP solution.
- Define Clear Data Security Policies: Establish comprehensive data security policies that align with your organization’s compliance requirements and risk tolerance. These policies should specify what data needs protection, how it should be handled, and the acceptable use of cloud resources.
- Choose the Right Deployment Model: Select the cloud DLP deployment model that best suits your needs. Options include agent-based solutions, API-based solutions, and network-based solutions. Consider factors like the cloud provider, the types of data you need to protect, and your existing security infrastructure.
- Start with a Phased Approach: Implement your cloud DLP solution in phases. Begin by monitoring and auditing data activity before enforcing strict policies. This allows you to identify potential issues and fine-tune your configurations without disrupting business operations.
- Integrate with Existing Security Tools: Integrate your cloud DLP solution with your existing security tools, such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems and cloud access security brokers (CASBs). This integration provides a unified view of your security posture and enables automated responses to security incidents.
- Provide User Training and Awareness: Educate your employees about data security policies and the importance of protecting sensitive information. Regular training and awareness programs can help reduce the risk of accidental data breaches.
- Monitor and Tune Your Solution: Continuously monitor your cloud DLP solution for effectiveness and adjust your policies and configurations as needed. Regularly review your data security policies to ensure they remain relevant and effective in the face of evolving threats.
- Establish Incident Response Procedures: Develop and document clear incident response procedures to address data security incidents. These procedures should Artikel the steps to take when a data breach is detected, including containment, eradication, and recovery.
- Consider Data Residency and Compliance: Ensure that your cloud DLP solution complies with data residency requirements and industry regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. Choose a solution that supports data storage and processing within the required geographic locations.
- Regularly Review and Update Policies: Data security threats and business needs change over time. Regularly review and update your DLP policies to stay ahead of evolving risks and adapt to new technologies and data usage patterns.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Integrating a Cloud DLP System
Integrating a cloud DLP system into an existing cloud infrastructure involves several key steps. Following a structured approach can help ensure a smooth and successful deployment.
- Planning and Assessment:
- Define your DLP goals and objectives.
- Identify sensitive data and its locations.
- Assess your current security infrastructure and identify integration points.
- Select a cloud DLP solution that meets your requirements.
- Deployment and Configuration:
- Install and configure the cloud DLP solution. This may involve deploying agents, configuring APIs, or setting up network monitoring.
- Configure data discovery and classification rules to identify sensitive data.
- Define data security policies and rules based on your organization’s needs.
- Configure user roles and permissions.
- Testing and Validation:
- Test the DLP solution to ensure it’s functioning correctly.
- Validate data discovery and classification accuracy.
- Test policy enforcement to ensure it’s working as expected.
- Conduct user acceptance testing (UAT) to gather feedback and make necessary adjustments.
- Training and Awareness:
- Train IT staff on how to manage and maintain the DLP solution.
- Educate end-users about data security policies and best practices.
- Conduct regular awareness campaigns to reinforce data security principles.
- Monitoring and Optimization:
- Monitor the DLP solution for performance and effectiveness.
- Analyze alerts and incidents to identify potential data breaches.
- Tune policies and configurations to optimize performance and reduce false positives.
- Regularly review and update data security policies to address evolving threats.
Recommendations for Ensuring Successful Cloud DLP Deployment
Successful cloud DLP deployment hinges on several key factors. By considering these recommendations, organizations can increase their chances of achieving their data security goals.
- Executive Sponsorship: Secure executive support for the cloud DLP initiative. This demonstrates the importance of data security and ensures that the project receives the necessary resources and support.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Foster collaboration between IT, security, compliance, and business teams. This ensures that the DLP solution aligns with the organization’s overall business objectives and regulatory requirements.
- Prioritize Data Discovery and Classification: Invest time and effort in accurate data discovery and classification. This is the foundation of effective DLP and enables you to apply the right policies to the right data.
- Focus on User Experience: Design DLP policies that minimize disruption to user workflows. Balance data security with usability to ensure that employees can perform their tasks efficiently.
- Automate Incident Response: Implement automated incident response workflows to streamline the handling of data security incidents. This can help reduce the time it takes to contain and remediate breaches.
- Stay Informed About Cloud Security Trends: Keep abreast of the latest cloud security threats and best practices. This enables you to proactively adapt your DLP solution to address emerging risks.
- Regularly Review and Update: Data security is an ongoing process. Regularly review and update your cloud DLP solution, policies, and procedures to ensure they remain effective.
- Leverage Cloud-Native Features: Take advantage of the cloud provider’s native security features to complement your DLP solution. This can enhance your overall security posture and streamline management.
- Consider Third-Party Expertise: If you lack in-house expertise, consider engaging a third-party consultant or managed security service provider (MSSP) to assist with the implementation and management of your cloud DLP solution.
- Document Everything: Maintain detailed documentation of your DLP implementation, including policies, configurations, and incident response procedures. This documentation is essential for compliance and troubleshooting.
Benefits of Using Cloud DLP Solutions
Implementing a cloud Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solution offers significant advantages for organizations, enhancing data security, streamlining compliance efforts, and improving overall operational efficiency. By leveraging the capabilities of cloud-based DLP, businesses can proactively protect sensitive information, reduce the risk of data breaches, and maintain regulatory adherence. This section will delve into the specific benefits of adopting cloud DLP, focusing on its impact on data security posture and compliance requirements.
Enhanced Data Security
Cloud DLP solutions significantly improve data security by providing comprehensive protection against data breaches and unauthorized access. These solutions offer a multi-layered approach to safeguarding sensitive data, covering various aspects of data protection.
- Data Discovery and Classification: Cloud DLP solutions automatically discover and classify sensitive data residing in the cloud environment. This includes identifying data types such as Personally Identifiable Information (PII), financial data, and intellectual property. This process helps organizations understand where their sensitive data resides and implement appropriate security controls.
- Real-time Monitoring and Incident Response: Cloud DLP continuously monitors data in motion and at rest, identifying potential data leakage incidents in real-time. When a policy violation occurs, the solution triggers alerts and initiates automated incident response actions, such as blocking the action, quarantining the data, or notifying security teams.
- Data Loss Prevention Policies: Organizations can define and enforce data loss prevention policies based on data types, user roles, and other criteria. These policies govern how data can be accessed, shared, and stored, minimizing the risk of accidental or malicious data loss. For instance, a policy might prevent employees from uploading sensitive financial documents to public cloud storage services.
- Encryption and Access Controls: Cloud DLP solutions often integrate with encryption and access control mechanisms. They can encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit, and enforce granular access controls to limit who can view, modify, or share specific data. This ensures that even if data is compromised, it remains protected and unusable by unauthorized individuals.
Improved Compliance and Regulatory Adherence
Cloud DLP solutions are instrumental in helping organizations meet compliance and regulatory requirements, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. By implementing a cloud DLP solution, businesses can streamline their compliance efforts and reduce the risk of non-compliance penalties.
- Compliance with Data Privacy Regulations: Cloud DLP helps organizations comply with data privacy regulations by enforcing policies that protect sensitive data. For example, a cloud DLP solution can monitor data access and usage, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access PII, and prevent the unauthorized transfer of personal data outside the organization.
- Automated Reporting and Auditing: Cloud DLP solutions provide automated reporting and auditing capabilities, enabling organizations to generate reports that demonstrate compliance with specific regulations. These reports track data access, usage, and movement, providing valuable insights for audits and compliance assessments.
- Data Retention and Disposal Policies: Cloud DLP solutions can enforce data retention and disposal policies, ensuring that data is stored and disposed of in accordance with regulatory requirements. This helps organizations avoid penalties associated with improper data handling and lifecycle management. For example, a cloud DLP solution can automatically delete sensitive data after a specified retention period, in compliance with GDPR.
- Reduced Risk of Fines and Penalties: By implementing a cloud DLP solution, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of fines and penalties associated with non-compliance. This is achieved by proactively protecting sensitive data, monitoring for policy violations, and demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements.
Improved Data Security Posture
Cloud DLP solutions improve an organization’s overall data security posture by providing a holistic approach to data protection. This includes enhancing visibility into data activity, reducing the attack surface, and strengthening the overall security infrastructure.
- Increased Visibility and Control: Cloud DLP solutions provide enhanced visibility into data activity across the cloud environment. This includes tracking data access, usage, and movement, enabling organizations to gain a comprehensive understanding of how data is being handled. This increased visibility allows for better control over data and the ability to identify and address potential risks.
- Reduced Attack Surface: Cloud DLP helps reduce the attack surface by identifying and mitigating potential vulnerabilities. This includes preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data, blocking malicious activities, and enforcing security policies. By proactively addressing these vulnerabilities, organizations can minimize the risk of successful attacks.
- Proactive Threat Detection and Prevention: Cloud DLP solutions proactively detect and prevent threats by monitoring data activity in real-time. This includes identifying and blocking malicious activities, such as data exfiltration attempts and unauthorized access to sensitive data. For instance, a cloud DLP solution might detect an attempt to download a large amount of sensitive data and automatically block the download.
- Integration with Other Security Tools: Cloud DLP solutions often integrate with other security tools, such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems and Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms. This integration enables organizations to centralize security monitoring, automate incident response, and improve the overall effectiveness of their security infrastructure.
Cloud DLP Solution Providers and Market Overview
The cloud data loss prevention (DLP) market is dynamic and competitive, with numerous vendors offering solutions tailored to the unique challenges of cloud environments. Understanding the key players and their offerings is crucial for organizations seeking to secure their data in the cloud. This section provides an overview of leading cloud DLP providers and the current market landscape.
Leading Providers of Cloud DLP Solutions
Several vendors have established themselves as leaders in the cloud DLP market, offering a range of features and functionalities to address data security needs. These providers often specialize in different aspects of cloud security, such as data discovery, classification, monitoring, and incident response.
- Microsoft: Microsoft offers a comprehensive DLP solution integrated within its Microsoft 365 suite, providing data protection across various cloud services like Exchange Online, SharePoint Online, and Microsoft Teams. Microsoft’s DLP capabilities include predefined and custom policies, sensitive information type detection, and incident management features. An example is the integration of DLP policies with Microsoft Purview to classify and protect sensitive data across the Microsoft cloud ecosystem.
- Forcepoint: Forcepoint provides a cloud-based DLP solution that focuses on data-centric security. Its offerings include data discovery, classification, and protection across various cloud applications and endpoints. Forcepoint emphasizes user behavior analytics (UBA) to identify and mitigate insider threats. An example of their product is Forcepoint DLP, which provides detailed data loss prevention capabilities.
- McAfee (Now Trellix): Trellix (formerly McAfee) offers a cloud DLP solution designed to protect data across various cloud environments. Trellix DLP provides data discovery, classification, and policy enforcement capabilities, along with features for incident response and remediation. An example is Trellix Data Loss Prevention, a comprehensive solution for cloud and on-premises environments.
- Broadcom (Symantec): Broadcom (Symantec) provides cloud DLP solutions as part of its broader security portfolio. Symantec DLP offers features such as data discovery, classification, and policy enforcement, with a focus on protecting sensitive data across cloud applications and endpoints. An example is Symantec DLP, which provides comprehensive data protection capabilities.
- Digital Guardian: Digital Guardian offers a cloud-delivered DLP solution that focuses on endpoint and cloud data protection. Its solution provides features such as data discovery, classification, and policy enforcement. An example is the Digital Guardian Data Loss Prevention platform, designed for comprehensive data protection.
- Proofpoint: Proofpoint offers a cloud-based DLP solution that focuses on protecting data from email-borne threats and insider risks. Its solution includes features such as data discovery, classification, and policy enforcement. An example is Proofpoint Information Protection, which provides email and data security capabilities.
Comparison of Cloud DLP Vendors
Different cloud DLP vendors offer unique strengths and capabilities, making it essential for organizations to carefully evaluate their options based on their specific needs and requirements. The following table compares some key aspects of leading cloud DLP solutions:
| Feature | Microsoft | Forcepoint | Trellix | Broadcom (Symantec) | Digital Guardian | Proofpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Cloud-native (Microsoft 365) | Cloud-based | Cloud-based | Cloud-based | Cloud-delivered | Cloud-based |
| Data Discovery | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Data Classification | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Policy Enforcement | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Incident Response | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| User Behavior Analytics (UBA) | Limited | Yes | Yes | Yes | Limited | Yes |
| Integration with Cloud Services | Excellent (Microsoft 365) | Good | Good | Good | Good | Good |
| Pricing Model | Subscription-based | Subscription-based | Subscription-based | Subscription-based | Subscription-based | Subscription-based |
Cloud DLP Market Landscape Overview
The cloud DLP market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing adoption of cloud services and the growing threat of data breaches. Several factors are influencing the market landscape:
- Market Growth: The cloud DLP market is expanding rapidly, with a projected growth rate fueled by the increasing need for data security in cloud environments. For instance, a report by Gartner predicts that the cloud security market will continue to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by the shift to cloud-based services.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, is a significant driver for cloud DLP adoption. Organizations must implement DLP solutions to protect sensitive data and avoid costly fines. For example, the implementation of GDPR has increased the demand for DLP solutions that can identify and protect personal data.
- Integration with Cloud Security Tools: Cloud DLP solutions are increasingly integrated with other cloud security tools, such as cloud access security brokers (CASBs) and security information and event management (SIEM) systems, to provide a comprehensive security posture. This integration enables organizations to gain greater visibility and control over their data.
- Focus on User Behavior Analytics (UBA): Vendors are incorporating UBA capabilities to detect and mitigate insider threats. UBA helps identify risky user behavior and prevent data loss incidents. For instance, Forcepoint’s focus on UBA helps identify anomalous user activity.
- Emerging Technologies: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being used to enhance DLP solutions, improving data classification accuracy and automating incident response. AI-powered DLP solutions can more effectively identify and protect sensitive data.
- Market Consolidation: The cloud DLP market is experiencing consolidation, with larger security vendors acquiring smaller DLP providers to expand their product offerings and market share. This trend is expected to continue as the market matures.
Future Trends in Cloud DLP
The landscape of data loss prevention in the cloud is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology, changes in cloud adoption models, and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. Understanding these trends is crucial for organizations to proactively protect their sensitive data. This section will explore the emerging forces shaping the future of cloud DLP and how solutions are adapting to meet these challenges.
Adapting to New Technologies and Cloud Models
Cloud DLP solutions are adapting to the continuous evolution of cloud computing, embracing new technologies and cloud deployment models. This adaptability is essential for maintaining effective data protection.
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Support: Organizations are increasingly adopting multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies to leverage the benefits of different cloud providers and deployment models. Cloud DLP solutions are evolving to provide consistent data protection across these diverse environments. This includes the ability to monitor and control data movement, apply consistent policies, and generate unified reports across various cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
- Serverless Computing Integration: Serverless computing is gaining popularity due to its scalability and cost-effectiveness. Cloud DLP solutions are integrating with serverless environments to protect data stored and processed in these architectures. This involves monitoring function invocations, analyzing data flows, and enforcing policies to prevent data leakage from serverless applications.
- Containerization and Kubernetes Support: Containerization technologies like Docker and orchestration platforms like Kubernetes are changing how applications are deployed and managed. Cloud DLP solutions are being adapted to secure data within containerized environments. This includes scanning container images for sensitive data, monitoring container network traffic, and enforcing DLP policies within Kubernetes clusters.
- Edge Computing Integration: As edge computing becomes more prevalent, cloud DLP solutions will need to extend their capabilities to protect data processed at the edge. This involves deploying DLP agents or appliances at edge locations to monitor and control data flow, even when connectivity to the central cloud is intermittent.
The Influence of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are playing an increasingly important role in the evolution of cloud DLP. These technologies enable more sophisticated and proactive data protection strategies.
AI and ML are used to analyze vast amounts of data, identify anomalies, and automate policy enforcement, leading to a more intelligent and effective approach to data loss prevention. The core function is to detect and respond to threats in real-time.
Imagine a visual representation of a cloud DLP solution enhanced by AI and ML. It could be depicted as a central hub, a virtual command center, receiving data streams from various sources within the cloud environment: file storage, databases, email systems, and network traffic. These streams converge at the hub, where AI-powered engines are actively at work. One engine, a “Data Pattern Recognition Engine,” is depicted as a complex neural network, constantly learning and adapting to identify sensitive data patterns.
This engine, represented with interconnected nodes and pathways, is continuously trained on both known and evolving data patterns, such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, and proprietary information. Another engine, a “Behavioral Analysis Engine,” visualizes user activity and data flows, identifying unusual or suspicious behavior. This engine is represented by a dynamic graph, showing user access patterns, data transfers, and potential data exfiltration attempts.
Unusual activities are highlighted in red, indicating potential risks. Both engines are linked to a “Policy Enforcement Engine,” which acts as the central control point. This engine, represented by a series of interlocking gears, is responsible for automatically enforcing DLP policies. The gears are interlocked, indicating that each action triggers another, ensuring that policies are applied consistently and effectively. The entire system is monitored by a “Threat Intelligence Dashboard,” which provides real-time insights into data security posture.
This dashboard displays key metrics, such as the number of incidents detected, the types of threats encountered, and the effectiveness of DLP policies. The dashboard is visualized as a dynamic display, with interactive charts and graphs that provide a clear overview of the data security landscape. This visual representation emphasizes the proactive and intelligent nature of AI-powered cloud DLP, demonstrating its ability to detect, analyze, and respond to data security threats in a dynamic cloud environment.
- Advanced Threat Detection: ML algorithms can analyze network traffic, user behavior, and data content to detect sophisticated threats that traditional DLP solutions might miss. For example, ML can identify insider threats by analyzing user activity patterns and flagging unusual behavior that could indicate data exfiltration attempts.
- Automated Policy Enforcement: AI can automate policy enforcement, reducing the need for manual intervention. For instance, AI can automatically classify sensitive data, apply appropriate security policies, and quarantine or block unauthorized data transfers.
- Anomaly Detection: ML algorithms can detect anomalies in data access patterns, such as unusual file access or data transfer activity, that could indicate a data breach. This enables organizations to proactively respond to potential threats before data is compromised.
- Contextual Awareness: AI can provide contextual awareness, understanding the context of data and user behavior to make more informed decisions. For example, AI can identify the sensitivity of a document based on its content, user, and location, allowing for more granular and effective policy enforcement.
- Reduced False Positives: ML can improve the accuracy of DLP solutions by reducing false positives. By learning from historical data and user behavior, ML can distinguish between legitimate and malicious activities, reducing the number of unnecessary alerts and improving the efficiency of security teams.
Last Point
In conclusion, understanding what is a data loss prevention (DLP) solution for cloud is paramount for organizations leveraging cloud services. From its core functionalities to its implementation strategies and future trends, cloud DLP is a dynamic field that continues to evolve. By embracing cloud DLP, businesses can fortify their data security posture, maintain compliance, and protect their valuable assets in an increasingly interconnected digital world.
The future of data security lies in proactively managing and securing data within the cloud, and cloud DLP is at the forefront of this evolution.
Questions and Answers
What is the main difference between on-premise DLP and cloud DLP?
On-premise DLP solutions are deployed within a company’s physical infrastructure, while cloud DLP solutions are designed specifically for cloud environments, providing monitoring and control over data stored and accessed in the cloud.
How does cloud DLP help with compliance?
Cloud DLP helps with compliance by enforcing data security policies, monitoring data movement, and providing reporting capabilities that demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
What types of data can cloud DLP protect?
Cloud DLP can protect various types of sensitive data, including personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, intellectual property, and confidential business information.
What are the common challenges in implementing cloud DLP?
Common challenges include integrating with various cloud services, configuring policies effectively, and ensuring minimal impact on user productivity. Complexity and cost are also considerations.